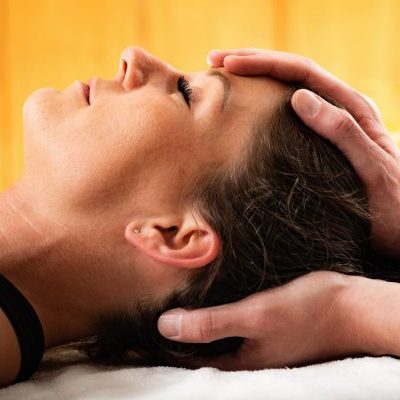

Physiotherapy
Within the physical therapy profession, manual therapy is defined as a clinical approach utilizing skilled, specific hands-on techniques,
including but not limited to manipulation/mobilization, used by the physical therapist to diagnose and treat soft tissues and joint structures for the purpose of modulating pain; increasing range of motion (ROM); reducing or eliminating soft tissue inflammation; inducing relaxation; improving contractile and non-contractile tissue repair, extensibility.
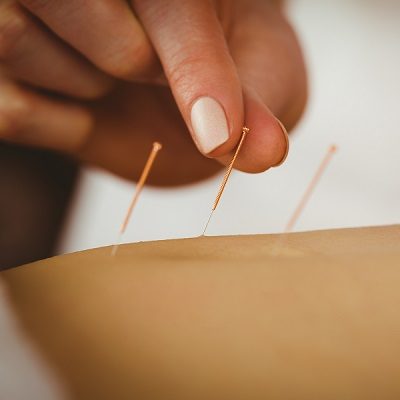
Acupuncture
Acupuncture is a key component of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) involving thin needles inserted into the body at acupuncture points.
It can be associated with the application of heat, pressure to these same points. Acupuncture is commonly used for pain relief, though it is also used for a wide range of other conditions. The benefits of acupuncture are sometimes difficult to measure, but many people find it helpful as a means to control a variety of painful conditions.
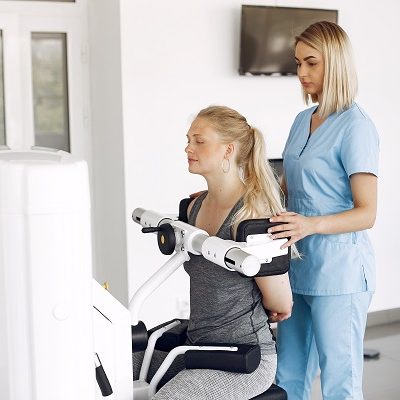


Active Rehab
Active rehabilitation is a program in which exercise and education are the foundations for therapy.
At Proactive physiotherapy, each training program is designed and carried out by a registered physiotherapist. On your first visit, the focus will be on completing a thorough assessment of your baseline strength and flexibility, and establishing your training goals. This will allows our physiotherapists to design a program that is safe and effective for you. Your program can include elements of core strengthening, postural re-education, functional training, cardiovascular endurance, and flexibility. Your physiotherapist will show you the core starting blocks which will be followed by an at home exercise program. On your subsequent visits, your physiotherapist will continually re-assess your program and make the necessary changes to help keep you on track and achieve your goals.
Intra Muscular Stimulation/IMS
The treatment involves dry needling of affected areas of the body without injecting any substance.
The needle sites can be at the epicenter of taut, tender muscle bands, or they can be near the spine where the nerve root may have become irritated and supersensitive. Penetration of a normal muscle is painless; however, a shortened, supersensitive muscle will ‘grasp’ the needle in what can be described as a cramping sensation.

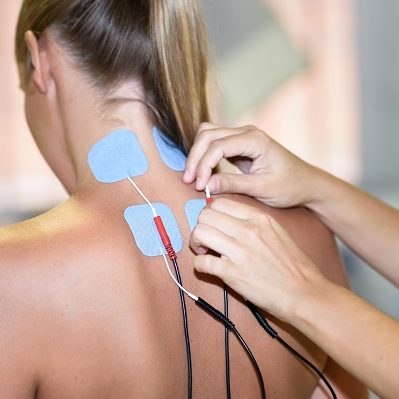
Electrotherapy
Electrotherapy is the use of electrical energy as a medical treatment.
The American Physical Therapy Association acknowledges the use of Electrotherapy for:
1. Pain management
2. Treatment of neuromuscular dysfunction
3. Improves range of joint mobility
4. Tissue repair
5. Acute and chronic edema
Soft Tissue Release/Massage
Myofascial Therapy targets the muscle and fascial systems, promotes flexibility and mobility of the body's connective tissues.
Likewise, it mobilizes fibrous adhesions and reduces the severity and sensitivity of scarring caused by injury or surgery. Massage techniques may be used as part of a treatment application. Referred to, in Soft Tissue Therapy, as broad-handed techniques, this mode of treatment aims to reduce swelling and/or inflammation.


Women's Health
When the pelvic floor muscles are low- tone (hypotonic), urinary or bowel incontinence, urgency and pelvic organ prolapse can occur.
These are NOT a normal part of aging and the muscles can become weak for many reasons. Following an assessment treatments include: Pelvic floor re-training and exercises Provision of pelvic floor educators/muscle stimulators to improve your activation and power of your pelvic floor contraction Pelvic stability exercises to strengthen the abdominal muscles.
Vestibular Therapy
Vestibular therapy is an exercise-based program, designed by a specialized physical therapist, to improve balance and reduce problems related to dizziness.
Patients typically referred for vestibular rehabilitation therapy are those diagnosed with dizziness, imbalance, vertigo, Meniere’s syndrome, benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV) and neck-related dizziness. Common symptoms that can be helped with vestibular rehabilitation include:
• Dizziness or blurry vision with head movements
• Neck tightness, stiffness, and/or pain
• Imbalance or the need to hold onto objects when walking
• Headaches
• Frequent falls
• Generalized “dizziness, wooziness and foggy head” feelings
• Vertigo/spinning

At your appointment, a physical therapist will evaluate your symptoms and review your medical history.
Your assessment will include all or part of the following areas:
• Balance and/or leg strength/flexibility
• Gait (how you walk)
• Visual stability and mobility
• Neck mobility and neck and arm strength
• Positional testing.
Patients are typically seen one to two times each week for 6 to 8 weeks, but this varies based on the patient’s diagnosis, severity of symptoms, and response to therapy. Some patients may be seen for only one to two sessions; other patients may need continued treatment for a few months. Many times, vestibular rehabilitation therapy will be the only treatment needed. In most cases, if patients continue to perform the exercises they have learned, balance and dizziness problems decrease significantly or completely disappear.

Concussion Therapy
A Concussion is a type of traumatic brain injury caused by a bump, blow, or jolt to the head or by a hit to the body that causes the head and brain to move rapidly back and forth.
Signs and symptoms of a concussion may not appear until hours or days after the injury. Common symptoms may include:
• Headache and Dizziness
• Light / Sound Sensitivity
• Nausea / Vomiting
• Balance problems
• Memory loss problems
• Generalized “dizziness, wooziness and foggy head” feelings
• Anxiety / Depression / Emotional imbalance
At your appointment, a physical therapist will evaluate your symptoms and review your medical history.
Your assessment will include all or part of the following areas:
• Oculomotor and Vestibular reflexes
• Visual Accommodation
• Access balance / Postural Sway
• Assessment of Cervical Spine
• TMJ, Thoracic Spine & Shoulder
Patients are typically seen one to two times each week for 6 to 10 weeks, but this varies based on the patient’s diagnosis, severity of symptoms, and response to therapy. Some patients may be seen for only one to two sessions; other patients may need continued treatment for a few months. In most cases, if patients continue to perform the exercises they have learned, balance and dizziness problems decrease significantly or completely disappear.
